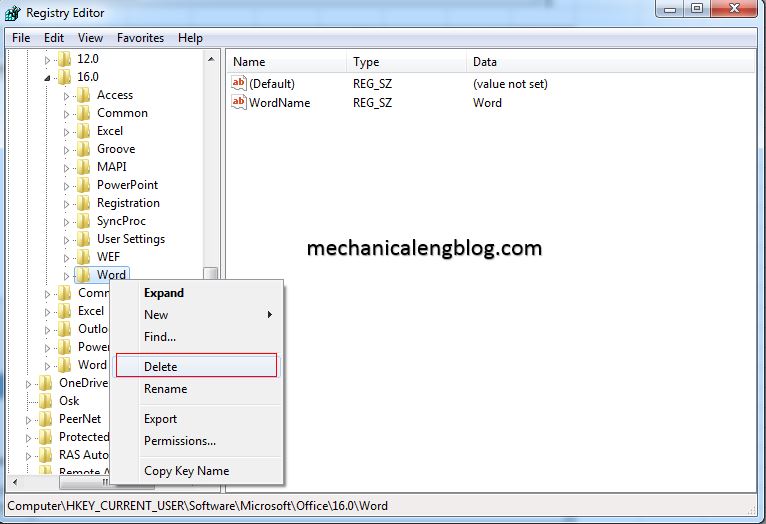
If you have a generic Microsoft Word 2007/2010/2013 problem, or you just changed your default font, borders and/or page size and you can’t remember how to undo those changes, you can easily reset your settings back to default by deleting some files. Please follow these steps: Delete Normal.DOTM and BuildingBlocks.DOTX: these files are rebuilt. If you have changed your default font, boarders, page size, and you can’t remember how to undo those changes or if you just have a weird Word 2007 2010 2013 problem, you can easily reset your settings back to default by deleting a few files. Before you begin, close Word. Delete NORMAL.DOTM and BUILDINGBLOCKS.DOTX. To reset Word to its default settings, however, you need only rename Normal.dotm (Normal.old is the usual suggestion). Word will generate a fresh factory-default copy the next time you start. If that doesn't solve your problems, then you may need to delete the Word Data key in the Registry.
- Restore Microsoft Word To Default Settings
- How To Reset Microsoft Office Word 2016 To The Default ...
- How To Reset Microsoft Word 2019 To Default Settings - YouTube

You can try to recover a Word document by:
If you're looking for information about how to recover other recent Office files, see the following articles:
If you can’t open the document, or the content in the document is damaged, see How to troubleshoot damaged documents in Word.
To find a lost document:
Search for Word documents
Try searching for the document in Windows:
- Select Start, type the document name (in Windows 8.1, type the name in the Search box), and then press Enter.
- If the Documents list (or Files list in Windows 8.1) contains the document, double-click the document to open it in Word.
If the search results don't contain the file, go to the next method.
Searching for Word backup files
Word backup file names have a '.wbk' extension. If you have the 'backup copy' option selected in Word, there might be a backup copy of the file.
To check whether this option is on, select File > Options > Advanced, scroll down to the Save section, and then select Always create backup copy.
If you have a Microsoft 365 subscription, check these two folder locations for a backup file:
- C:Users<UserName>AppDataRoamingMicrosoftWord
- C:Users<UserName>AppDataLocalMicrosoftOfficeUnsavedFiles
Note: In these paths, replace <UserName> with your username.
To find the backup copy of the file, select Start, enter .wbk in the Search box, and then press Enter. If you find any files that have the name 'Backup of' followed by the name of the missing file, double-click the file name to open it.
If you don’t find a backup file for the document, go to the next method.
Checking the Recycle Bin
If you deleted a Word document without emptying the Recycle Bin, you might be able to restore the document.
- Double-click the Recycle Bin on the Desktop.
- Search through the list of documents to see whether the deleted Word document is still there. If you don't know the file name, look for file types such as .doc, .docx, and .dot.
- If you find the desired Word file, right-click the file name, and then select Restore to recover the file.
If you don't find the desired file, go to the next method.
Windows File Recovery Tool
If you are using Windows 10, version 2004 or later, you can try the Windows File Recovery tool. Windows File Recovery is available from the Microsoft Store. You can use it to recover files that have been permanently deleted. For more information about this tool, see Recover lost files on Windows 10.

Restoring documents saved to SharePoint and OneDrive
For documents that you saved or synced to SharePoint, see Restore items in the recycle bin that were deleted from SharePoint or Teams.
For documents that you saved or synced to OneDrive, see Restore deleted files or folders in OneDrive.

To find missing content or a newer version:
Word takes different actions to protect your changes in Word documents:
If Word opens a document from SharePoint or OneDrive, the program uses AutoSave to save changes to the “cloud” document. We recommend that you leave the AutoSave feature set to On.
If Word opens a document from your local disk or network shared folder, Word uses AutoRecover to save changes to an AutoRecover file. The default AutoRecover save interval is 10 minutes. We recommend that you leave the AutoRecover feature set to On.
Restarting Word to open AutoRecover files
Word searches for AutoRecover files every time it starts. Therefore, you can try using the AutoRecover feature by closing and reopening Word. If Word finds any automatically recovered file, the Document Recovery task pane opens, and the missing document should be listed as 'document name [Original]' or as 'document name [Recovered].' If this occurs, double-click the file name in the Document Recovery pane, select File > Save as, and then save the document as a .docx file. To manually change the extension to .docx, right-click the file, and select Rename.
Note In Microsoft 365 Subscription, when Word starts, it searches for AutoRecover files. If any recovered files are found, Word opens them by having a Message Bar. Select Save to save the recovered file as a .docx file. If there are many recovered files, Word usually opens the last-changed files, and puts the remaining files into the Document Recovery task pane.
Searching for AutoRecover files
If you have a Microsoft 365 subscription, check the following folder locations for backup files:
Restore Microsoft Word To Default Settings

- C:Users<UserName>AppDataRoamingMicrosoftWord
- C:Users<UserName>AppDataLocalMicrosoftOfficeUnsavedFiles
Note: In these paths, replace <UserName> with your username.
If you don’t find the missing file in these locations, open Word, and select File > Info > Manage Document > Recover Unsaved Documents.
If you still haven’t found the file, try manually searching for AutoRecover files. To do this, select Start, enter .asd in the Search box, then press Enter.
If you find any files that have the .asd extension, follow these steps:
- Open Word, and then go to File > Open > Browse.
- In the files of type list to the right of File name, select All Files.
- Right-click the backup file that you found, and then select Open.
If there are no .asd files, go to the next method.
How To Reset Microsoft Office Word 2016 To The Default ...
Searching for temporary files
Temporary file names have a .tmp extension. To find these files, follow these steps:
How To Reset Microsoft Word 2019 To Default Settings - YouTube
- Select Start, type .tmp (in Windows 8.1, type .asd in the Search box), and then press Enter.
- Select the Documents tab.
- Scroll through the files to search for file names that match the last few dates and times that you edited the document.
- If you find the missing file, go to step 4.
- If you don’t find the file, repeat steps 1 through 3, but search on the tilde character (~) instead of .tmp (temporary file names start with a tilde).
- In Word, go to File > Open, and then select the Folders tab.
- Navigate to or search for the folder where you found the .tmp file, and then select the folder name to open the folder contents pane.
- At the top of the pane, select the name of the folder. This opens File Explorer.
- In File Explorer, change the file type (next to the file name field, near the bottom) to All files.
- Open the .tmp file.
References