GeoGebra Publisher's Description. GeoGebra is free and multi-platform dynamic mathematics software for all levels of education that joins geometry, algebra, tables, graphing, statistics and calculus in one easy-to-use package. It has received several educational software awards in Europe and the USA. We were unable to load Disqus. GeoGebra for Teaching and Learning Math Free digital tools for class activities, graphing, geometry, collaborative whiteboard and more. Open a new Geogebra File. Options - Settings - Graphics - x Axis - Units - pi - Save settings - Close 3.
Tutorial:New features of Version 4.2
GeoGebra 4.2 will be released soon. 21 developers have contributed to this release, so there are many new and exciting features to explore and enjoy! Here are some of the things you can look forward to, and details of how to try out the Release Candidate are here.
Speed & Stability
Sim girls full game. As well as the usual bug-fixing and adding features, while developing version 4.2 we have rewritten large parts of GeoGebra so that it will be much more stable and also faster (much faster in some cases) than previous versions.In particular, the following will be much faster:
- anything using the Sequence command
- the following commands when used on polynomials: Derivative/Integral/Tangent/Degree/Coefficients/Expand
Here is an example of a file using Derivative[ ] that is much faster in GeoGebra 4.2.
Here is a demonstration of volume of revolution running in GeoGebra 4 and here is the same file in GeoGebra 4.2. Drag the red point marked “View3D” to see how much faster it is.
CAS View
The long awaited view for symbolic calculations is here. It allows you to symbolically factor, expand, differentiate or integrate expressions that may include parameters, and it is dynamically connected to all the other views. The documentation is available at CAS View.
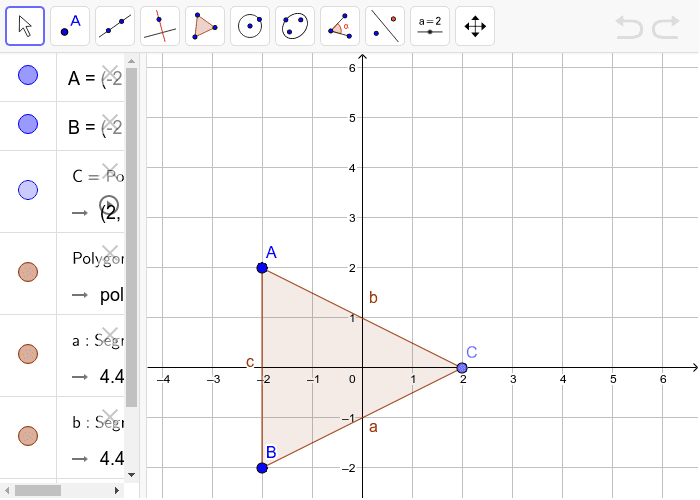
Here is an example showing how the CAS View interacts with the Graphics View.
Drag the points A, B, C to see the exact calculation of the coordinates change.
Features
The feature that’s taken the most programming time in this release is that worksheets can now be viewed on devices without Java (eg iPads, Android Tablets, Chromebooks). The best way to make use of this is to upload your applets to GeoGebra (File -> Share) and then the conversion will be done automatically.
At the moment only the Graphics View is supported. You can test how worksheets will look and behave on tablets by adding ?mobile=true on the end of the URL in GeoGebra, eg:
http://www.geogebra.org/student/m20510?mobile=trueTools
The Pen Tool has been enhanced so that it now creates a PolyLine rather than drawing to a bitmap. Together with new Delete Tool (drag a “rubber” to delete) it’s now much easier & better to use.
You can now drag a parabola, but keep its vertex fixed. Just hold down Alt Hunter tools dsp 600 manual. when dragging!
The Rigid Polygon Tool has been enhanced with a small but useful feature: simply click on a polygon to make a “rigid” copy of it (ie the copy can be rotated and translated by dragging)
Geogebra 4.2
Neel Shah, as part of Google Summer of Code, has programmed some shape recognition algorithms for the Freehand Shape Tool, which will recognize circles, lines, line segments, triangles and quadrilaterals. It works very well on an interactive whiteboard (IWB).
Geogebra 4.2 Download
You may also check details of the hundreds of changes in the GeoGebra 4.2 Release Notes.
Power
Kai Chung Tam has programmed the PSLQ algorithm for us in Java which allows a Surd to be numerically reconstructed from a decimal. So for example SurdText[2.414213562373095] returns a nice FormulaText ie sqrt{2}+1. See here for an example.
We have made it much easier to make worksheets with slopefields and the particular integral like this.
All you need to type is:f(x,y)=x/y
SlopeField[f]
A=(1,1)
Locus[A,f]
If you need more control over the spacing, there are some options, see the SlopeField Command in the manual.
Geogebra 4d
A new command has been added: LocusEquation. This will calculate the equation of a (geometrical) locus using Gröbner bases.
For example. here is the (numerical) locus of a parabola with the calculated (exact) locus overlaid.